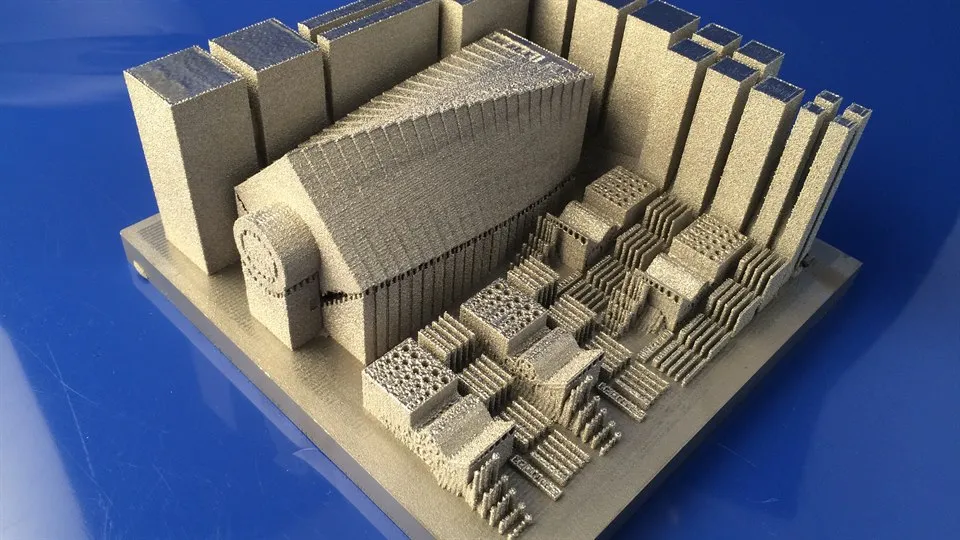
Demonstration of additive manufacturing as a method for fabrication of 316L‑Grade Components
The aim of the project is to test electron beam melting (EBM) as a potential method for the production of stainless steel components for a fusion reactor in France.
In the field of additive manufacturing, larger complex components cannot be developed today. The aim of the project is to show how a breakdown of the final part can be produced in stainless steel using EBM as well as a subsequent fusion treatment to merge the different parts.
The project looks at the development from process optimization, manufacturing, evaluation of the test components to demonstration of manufacturing of divided parts and delivery to joining. The technical solution for the joining of the details made by additive manufacturing will require new types of construction solutions and a tailor-made heat treatment process for the joint.
Facts ITER:
The ITER project is about testing large-scale fusion power for the first time. When fusion energy is extracted, heat is generated up to 150 million degrees. In order to handle this, many large, advanced and extremely durable components are required and the challenge is to create a cost-effective manufacturing process for them. ITER is an experimental plant for fusion technology operated by the EU, USA, Russia, Japan, China, India and South Korea. The test facility, which is being built in southern France, is estimated to cost about SEK 160 billion and the EU contributes about half of this.
Facts
Project period
150101—170101
Research centers
Project leader